The Importance of Control of Stored Grain Pest in Modern Agriculture
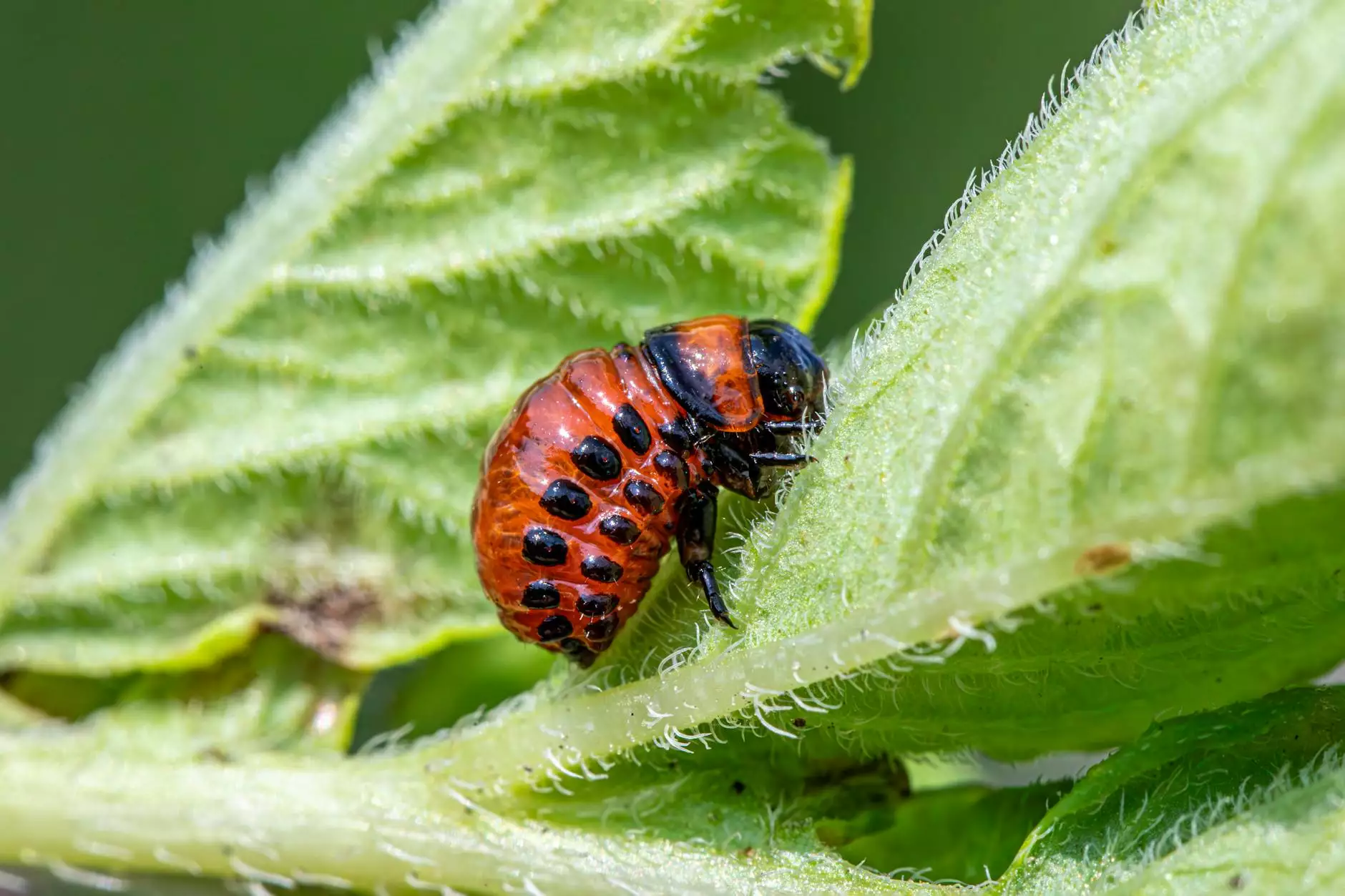

Grain storage is a critical component of modern agriculture. The control of stored grain pest is vital to maintain the quality and safety of harvested grains. Without proper management, pests can wreak havoc, leading to significant losses in yield and quality. This article delves into the essential strategies for pest control that farmers can adopt to protect their investments and ensure a successful crop season.
Understanding Stored Grain Pests
Stored grain pests are insects that infest stored grains, including wheat, corn, barley, and rice. These pests thrive in the warm and humid environments typical of grain storage facilities. Common pests include:
- Grain weevils: Small beetles that feed on grains, leading to structural damage.
- Indian meal moths: Moths that infest various stored products, causing contamination.
- Rust-red flour beetles: Often found in flour and its products, they can compromise grain quality.
- Rice weevils: Known for damaging rice and other stored grains.
Signs of Infestation
Recognizing the signs of infestation is crucial for the control of stored grain pest. Here are a few indicators that can help farmers detect pest presence:
- Visible insects in stored grain or packaging.
- Webbing or silk around grains, indicating moth activity.
- Holes or tunneling in grain kernels, a sign of weevil activity.
- Unpleasant odors that might indicate mold or decay.
Integrated Pest Management Strategies
The most effective approach for the control of stored grain pest is Integrated Pest Management (IPM). This strategy combines multiple methods to minimize pest damage sustainably. Here are key components of IPM:
1. Monitoring and Surveillance
Regular monitoring of stored grains is essential. Farmers should:
- Inspect storage areas frequently for signs of pests.
- Use pheromone traps to catch male moths and assess the pest population.
- Keep records of pest sightings to identify trends and inform management practices.
2. Sanitation
Good sanitation practices can significantly reduce the risk of infestations. Farmers should:
- Clean storage bins and surrounding areas regularly.
- Remove all spilled grains and organic debris that can harbor pests.
- Use vacuuming and sweeping to eliminate potential breeding grounds.
3. Proper Storage Conditions
Creating a hostile environment for pests involves:
- Maintaining optimal moisture levels in stored grain—ideally below 14% moisture content.
- Controlling temperature with effective ventilation systems to discourage pest activity.
- Using airtight containers to limit pest access.
4. Chemical Control Options
When pest populations exceed tolerable thresholds, chemical control may be necessary. Farmers should:
- Choose products specifically labeled for stored grain pests.
- Apply treatments according to label instructions to ensure safety and compliance.
- Consider using grain protectants that can be applied directly to the grain before storage.
Biological Control Methods
Biological control leverages natural predators and parasites to combat stored grain pests. Options include:
- Beneficial insects: Introducing natural enemies, such as parasitic wasps that target pest larvae.
- Utilizing microbial insecticides that specifically target insect pests while sparing beneficial organisms.
Emerging Technologies in Pest Control
As agriculture evolves, so do the methods for control of stored grain pest. New technologies that show promise include:
- Smart sensors: Devices that monitor environmental conditions of storage facilities in real time.
- Biopesticides: Derived from natural materials, these products offer a less harmful alternative to conventional chemicals.
- Genetic control: Research into genetically modified organisms that are resistant to pest infestations.
The Economic Impact of Pest Control
Effective pest control directly influences a farmer's bottom line. The costs associated with pest infestations can be staggering, including:
- Financial losses from reduced quality and quantity of grain.
- Increased costs for pest management and mitigation efforts.
- Potential loss of market access for contaminated products.
Thus, investing in preventive measures and pest control strategies not only protects grain but also enhances overall profitability.
Conclusion: Ensuring Crop Success through Pest Control
The control of stored grain pest is non-negotiable in safeguarding grain quality and maintaining high agricultural standards. By applying integrated pest management practices, monitoring conditions, and utilizing advancements in pest control technology, farmers can protect their harvests and sustain their operations. Proactive pest management is essential for anyone aiming to achieve success in the ever-challenging landscape of agriculture. Partnering with industry leaders like TSGC INC can provide access to cutting-edge farm equipment repair and farming equipment that supports these crucial pest management strategies.